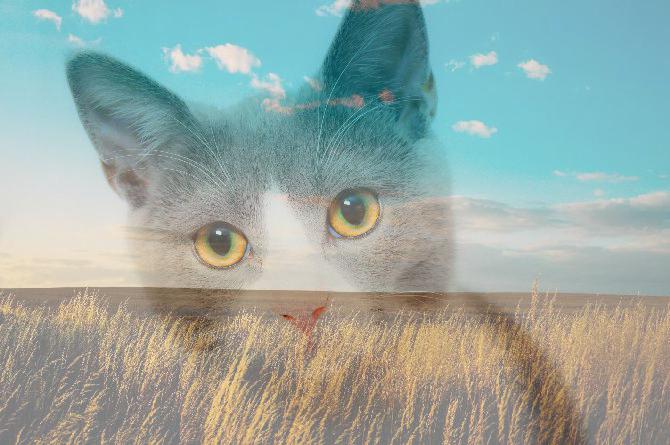
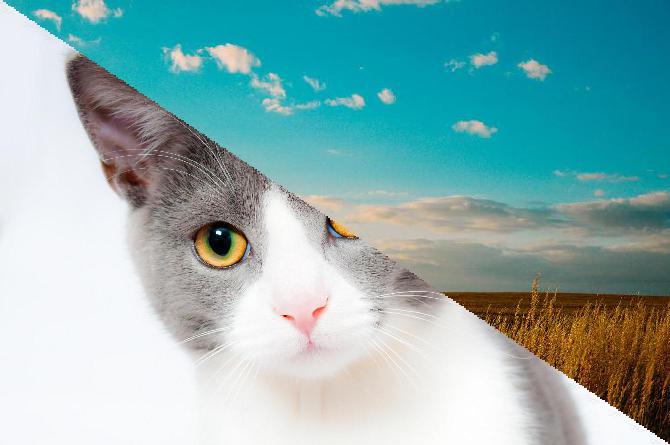
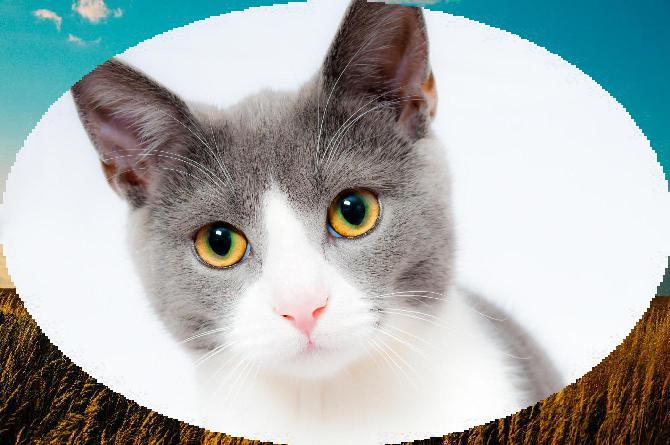
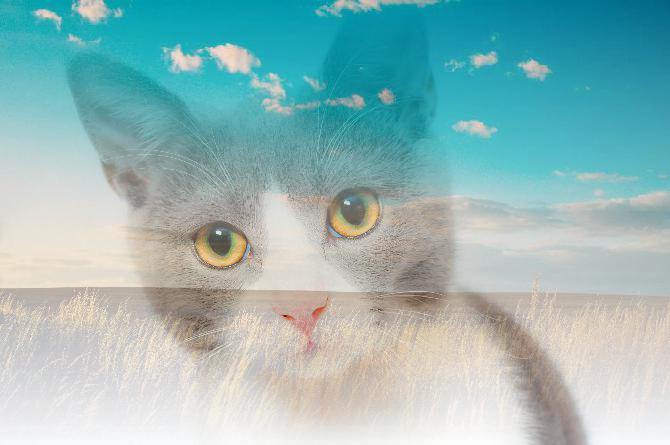
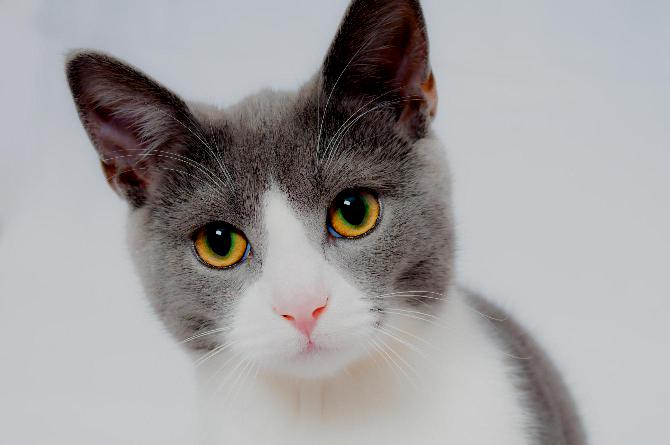
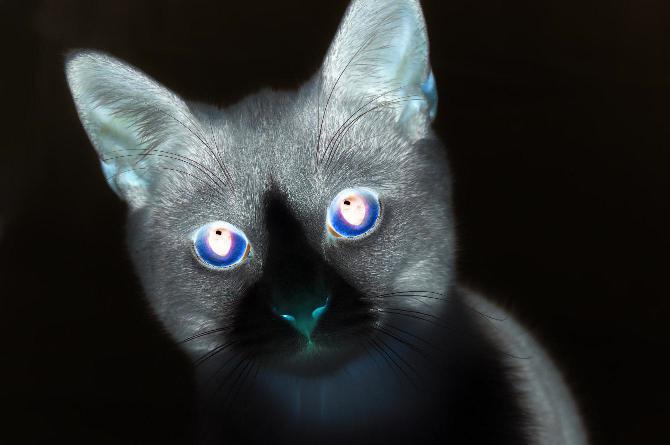
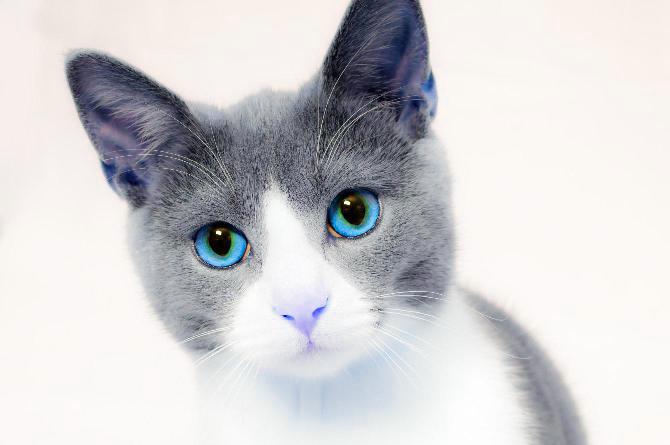
Image Module - Functions¶
Note
All source images in this document are derived from https://www.pexels.com (CC0 License).
Open images, Constructing images¶
open¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.open, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.open
Opens and identifies the given image file name:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> img = Image.open("data/srcimg01.jpg")
>>> # ... (do something to img) ...
>>> img.show() # invoke image viewer for debugging
>>> img.save("out.jpg") # save
>>>
You can also use file-like object like io.BytesIO (the file object must implement read(), seek(), and tell() methods, and be opened in binary mode.):
>>> from io import BytesIO
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> img1 = Image.open("source/_static/exams/data/srcimg09.png")
>>> imgdata = BytesIO()
>>> img1.save(imgdata, "PNG")
>>>
>>> # You can also use file-like object like io.BytesIO.
>>> img2 = Image.open(imgdata)
>>>
>>> # identical?
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.all(np.array(img1.getdata()) == np.array(img2.getdata()))
True
>>>
>>> from io import BytesIO
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> xpmsrc = b"""\
... /* XPM */
... static char * cross_xpm[] = {
... "8 8 2 1",
... "* c #0000ff",
... ". c #ffffff",
... "..****..",
... "..*..*..",
... "********",
... "*.*..*.*",
... "*.*..*.*",
... "********",
... "..*..*..",
... "..****..",
... };
... """
>>> img = Image.open(BytesIO(xpmsrc))
>>> mg.resize((8*10, 8*10)).save("cross.png")
See also: save.
new¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.new, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.new
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> img = Image.new("RGB", (640, 480)) # mode, size, color(default: 0)
>>> # ... (do something to img) ...
>>> img.show() # invoke image viewer for debugging
>>> img.save("out.jpg") # save
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> img = Image.new("RGB", (640, 480), (127, 127, 0)) # mode, size, color(default: 0)
>>> # ... (do something to img) ...
>>> img.show() # invoke image viewer for debugging
>>> img.save("out.jpg") # save
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> img = Image.new("RGB", (640, 480), "#ff00ff") # mode, size, color(default: 0)
>>> # ... (do something to img) ...
>>> img.show() # invoke image viewer for debugging
>>> img.save("out.jpg") # save
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> img = Image.new("L", (640, 480), 192) # mode, size, color(default: 0)
>>> # ... (do something to img) ...
>>> img.show() # invoke image viewer for debugging
>>> img.save("out.jpg") # save
For color, see ImageColor, and for mode, see Modes.
fromarray¶
Examples for single band¶
From numpy ‘C’ array (row major order) with dtype=np.uint8:
>>> # example for single band, from numpy 'C' array (row major order) with dtype=np.uint8
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> rawpb = np.arange(1, 3 * 2 + 1, dtype=np.uint8).reshape((2, 3))
>>> rawpb
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=uint8)
>>> rawpb.strides
(3, 1)
>>> rawpb.flags
C_CONTIGUOUS : True
F_CONTIGUOUS : False
OWNDATA : False
WRITEABLE : True
ALIGNED : True
UPDATEIFCOPY : False
>>>
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb)
>>> img.mode, img.size # interpreted as "L"
('L', (3, 2))
>>>
>>> list(img.getdata())
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
Passing the Image object to numpy.asarray returns the array which you can pass to Image.fromarray:
>>> # example for single band, from numpy 'C' array
>>> # (the case which L values are represented by 8bit integers)
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> img = Image.open("data/srcimg01.jpg").convert("L")
>>> rawpb = np.asarray(img)
>>> rawpb[0]
array([231, 232, 233, 233, 234, 235, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236,
236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 237, 237, 238, 238, 238, 237, 237,
237, 237, 237, 237, 237, 237, 235, 236, 236, 236, 236, 235, 234,
233, 235, 234, 233, 232, 230, 229, 228, 227, 229, 228, 228, 227,
--- snip ---
236, 237, 237, 238, 238, 237, 237, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236,
236, 236, 236, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235,
235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 235, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236, 236,
236, 237, 237, 237, 237, 237, 237], dtype=uint8)
>>>
>>> #
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb)
>>> img.mode, img.size # interpreted as "L"
('L', (670, 445))
>>>
>>> list(img.getdata())[:10]
[231, 232, 233, 233, 234, 235, 236, 236, 236, 236]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")[:20]
b'\xe7\xe8\xe9\xe9\xea\xeb\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xec\xed'
>>>
>>> for y in range(img.height // 100):
... for x in range(img.width // 100):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
231, 232, 233, 233, 234, 235,
232, 232, 233, 234, 235, 235,
233, 233, 233, 234, 235, 235,
233, 234, 234, 235, 235, 236,
From numpy ‘C’ array (row major order) without passing dtype:
>>> # example for single band, from numpy 'C' array (row major order)
>>> # Note that this example depends on the endian of your machine.
>>> # (The result of this example is of little-endian.)
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> rawpb = np.arange(1, 3 * 2 + 1).reshape((2, 3))
>>> rawpb
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
>>> rawpb.strides
(12, 4)
>>> rawpb.flags
C_CONTIGUOUS : True
F_CONTIGUOUS : False
OWNDATA : False
WRITEABLE : True
ALIGNED : True
UPDATEIFCOPY : False
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb)
>>> img.mode, img.size # interpreted as "I"
('I', (3, 2))
>>> list(img.getdata())
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x01\x00\x00\x00\x02\x00\x00\x00\x03\x00\x00\x00\x04\x00\x00\x00\x05\x00\x00\x00\x06\x00\x00\x00'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
>>>
From numpy ‘F’ array (column major order) with dtype=np.uint8:
>>> # example for single band, from numpy 'F' array (column major order) with dtype=np.uint8
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> rawpb = np.asfortranarray(np.arange(1, 3 * 2 + 1, dtype=np.uint8).reshape((2, 3)))
>>> rawpb
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=uint8)
>>> rawpb.strides
(1, 2)
>>> rawpb.flags
C_CONTIGUOUS : False
F_CONTIGUOUS : True
OWNDATA : True
WRITEABLE : True
ALIGNED : True
UPDATEIFCOPY : False
>>>
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb)
>>> img.mode, img.size # interpreted as "L"
('L', (3, 2))
>>>
>>> list(img.getdata())
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
If you want to do the other conversion pattern, unfortunately there is not the documetaion for it, so see _fromarray_typemap in PIL.Image.py.
Examples for multiple bands¶
From numpy ‘C’ array (the case which RGB values are represented by three 8bit integers):
>>> # example for multiple bands, from numpy 'C' array
>>> # (the case which RGB values are represented by three 8bit integers)
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> rawpb = np.arange(1, 2 * 4 * 3 + 1, dtype=np.uint8).reshape((4, 2, 3))
>>> rawpb
array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]],
[[13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18]],
[[19, 20, 21],
[22, 23, 24]]], dtype=uint8)
>>> # (__array_interface__['typestr'] is '|u1')
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb, "RGB")
>>> img.mode, img.size
('RGB', (2, 4))
>>> list(img.getdata(band=0))
[1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=1))
[2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=2))
[3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06\x07\x08\t\n\x0b\x0c\r\x0e\x0f\x10\x11\x12\x13\x14\x15\x16\x17\x18'
>>>
>>> for y in range(4):
... for x in range(2):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6),
(7, 8, 9), (10, 11, 12),
(13, 14, 15), (16, 17, 18),
(19, 20, 21), (22, 23, 24),
Passing the Image object to numpy.asarray returns the array which you can pass to Image.fromarray:
>>> # example for multiple bands, from numpy 'C' array
>>> # (the case which RGB values are represented by three 8bit integers)
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> img = Image.open("data/srcimg01.jpg")
>>> rawpb = np.asarray(img)
>>> rawpb[0]
array([[229, 232, 237],
[230, 233, 238],
[231, 234, 239],
...,
[232, 239, 247],
[232, 239, 247],
[232, 239, 247]], dtype=uint8)
>>> # (__array_interface__['typestr'] is '|u1')
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb, "RGB")
>>> img.mode, img.size
('RGB', (670, 445))
>>> list(img.getdata(band=0))[:10]
[229, 230, 231, 231, 232, 233, 234, 234, 234, 234]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=1))[:10]
[232, 233, 234, 234, 235, 236, 237, 237, 237, 237]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=2))[:10]
[237, 238, 239, 239, 240, 241, 242, 242, 242, 242]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")[:20]
b'\xe5\xe8\xed\xe6\xe9\xee\xe7\xea\xef\xe7\xea\xef\xe8\xeb\xf0\xe9\xec\xf1\xea\xed'
>>>
>>> for y in range(img.height // 100):
... for x in range(img.width // 100):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
(229, 232, 237), (230, 233, 238), (231, 234, 239), (231, 234, 239), (232, 235, 240), (233, 236, 241),
(230, 233, 238), (230, 233, 238), (231, 234, 239), (232, 235, 240), (233, 236, 241), (233, 236, 241),
(231, 234, 239), (231, 234, 239), (231, 234, 239), (232, 235, 240), (233, 236, 241), (233, 236, 241),
(231, 234, 239), (232, 235, 240), (232, 235, 240), (233, 236, 241), (233, 236, 241), (234, 237, 242),
From numpy ‘C’ array (the case which RGBA values are represented by 32bit integer):
>>> # example for multiple bands, from numpy 'C' array
>>> # (the case which RGBA values are represented by 32bit integer)
>>> # Note that this example depends on the endian of your machine.
>>> # (The result of this example is of little-endian.)
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> #
>>> rawpb_r = np.arange(1, 2 * 4 + 1).reshape((4, 2)) * 1
>>> rawpb_g = np.arange(1, 2 * 4 + 1).reshape((4, 2)) * 3
>>> rawpb_b = np.arange(1, 2 * 4 + 1).reshape((4, 2)) * 5
>>> rawpb_r
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
>>> rawpb_g
array([[ 3, 6],
[ 9, 12],
[15, 18],
[21, 24]])
>>> rawpb_b
array([[ 5, 10],
[15, 20],
[25, 30],
[35, 40]])
>>> rawpb = rawpb_r + (rawpb_g << 8) + (rawpb_b << 16)
>>> # (__array_interface__['typestr'] is '<i4' (32bit))
>>> img = Image.fromarray(rawpb, "RGBA")
>>> img.mode, img.size
('RGBA', (2, 4))
>>> list(img.getdata(band=0))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=1))
[3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=2))
[5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x01\x03\x05\x00\x02\x06\n\x00\x03\t\x0f\x00\x04\x0c\x14\x00\x05\x0f\x19\x00\x06\x12\x1e\x00\x07\x15#\x00\x08\x18(\x00'
>>>
>>> for y in range(4):
... for x in range(2):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
(1, 3, 5, 0), (2, 6, 10, 0),
(3, 9, 15, 0), (4, 12, 20, 0),
(5, 15, 25, 0), (6, 18, 30, 0),
(7, 21, 35, 0), (8, 24, 40, 0),
If you want to do the other conversion pattern, unfortunately there is not the documetaion for it, so see _fromarray_typemap in PIL.Image.py.
frombytes¶
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>>
>>> img1 = Image.open("data/srcimg01.jpg")
>>> img1.mode, img1.size
('RGB', (670, 445))
>>> # WARN: if you want to copy, use 'copy' method of Image object.
>>> # This is just example for frombytes!
>>> img2 = Image.frombytes(img1.mode, img1.size, img1.tobytes("raw"))
>>>
>>>
>>> # identical?
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.all(np.array(img1.getdata()) == np.array(img2.getdata()))
True
>>>
Example for single band:
>>> # example for single band
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> rawpb = b'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
>>> img = Image.frombytes("L", (3, 2), rawpb)
>>> list(img.getdata())
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
0, 1, 2,
3, 4, 5,
>>>
Example for multiple bands:
>>> # example for multiple bands
>>> from __future__ import print_function
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>>
>>> # --------------------------------------------------------------------
>>> # following codes are from `six <https://pypi.python.org/pypi/six/>`_.
>>> import sys
>>> import operator
>>> if sys.version_info[0] == 3: # python 3.x
... import struct
... int2byte = struct.Struct(">B").pack
... indexbytes = operator.getitem
... else: # python 2.x
... int2byte = chr
... def indexbytes(buf, i):
... return ord(buf[i])
... #
... # --------------------------------------------------------------------
...
>>>
>>> rawpb_r = b'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
>>> rawpb_g = b'\xa0\xa1\xa2\xa3\xa4\xa5'
>>> rawpb_b = b'\xf0\xf1\xf2\xf3\xf4\xf5'
>>>
>>> rawpb = b"".join([int2byte(indexbytes(rawpb_r, i))
... + int2byte(indexbytes(rawpb_g, i))
... + int2byte(indexbytes(rawpb_b, i))
... for i in range(len(rawpb_r))])
>>>
>>> img = Image.frombytes("RGB", (3, 2), rawpb)
>>> list(img.getdata())
[(0, 160, 240), (1, 161, 241), (2, 162, 242), (3, 163, 243), (4, 164, 244), (5, 165, 245)]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=0)) # R
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=1)) # G
[160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165]
>>> list(img.getdata(band=2)) # B
[240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245]
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
b'\x00\xa0\xf0\x01\xa1\xf1\x02\xa2\xf2\x03\xa3\xf3\x04\xa4\xf4\x05\xa5\xf5'
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
(0, 160, 240), (1, 161, 241), (2, 162, 242),
(3, 163, 243), (4, 164, 244), (5, 165, 245),
>>>
Example for “xbm” decoder:
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> xbmsrc = b"""\
... #define image_width 51
... #define image_height 24
... static char image_bits[] = {
... 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,
... 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,0xff,
... 0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0x07,0xff,0xff,0xff,
... 0xfc,0xff,0xf9,0x07,0xff,0xff,0x3f,0xfc,0x7f,0xf8,0x07,0xc1,0x83,0xcf,0xfd,
... 0x9f,0xfb,0x07,0xf7,0xef,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xef,0xf7,0xff,0xfd,0xff,
... 0xfb,0x07,0xef,0xf7,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xdf,0xfb,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,
... 0x07,0xbf,0xfd,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0x7f,0xfe,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,
... 0x7f,0xfe,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0x7f,0xfe,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xbf,
... 0xfd,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xdf,0xfb,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xef,0xf7,
... 0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xf7,0xef,0xff,0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xf7,0xef,0xff,
... 0xfd,0xff,0xfb,0x07,0xfb,0xdf,0x0f,0x80,0x1f,0x00,0x07,0xc1,0x07,0xff,0xff,
... 0xff,0xff,0x07
... };
... """
>>> img = Image.frombytes("1", (51, 24), xbmsrc, decoder_name="xbm")
>>> img.show()
fromstring¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.fromstring, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.fromstring
This method that have been marked as deprecated for many releases have been removed at Pillow 3.0.0 (actually is still defined but raise NotImplementedError). Use frombytes() instead. (But also note that original PIL has no frombytes but has only fromstring.)
frombuffer¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.frombuffer, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.frombuffer
Example for single band (cause warning in Pillow 4.1.x):
>>> # example for single band
>>> from PIL import Image
>>>
>>> rawpb = bytearray(b'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05')
>>>
>>> #
>>> img = Image.frombuffer("L", (3, 2), rawpb, 'raw') # cause warning in Pillow 4.1.x.
__console__:1: RuntimeWarning: the frombuffer defaults may change in a future release; for portability, change the call to read:
frombuffer(mode, size, data, 'raw', mode, 0, 1)
>>> # the above is identical to (in Pillow 4.1.x.): # may change in a future release
>>> # img = Image.frombuffer("L", (3, 2), rawpb, 'raw', 0, -1)
>>> list(img.getdata()) # data is imported with "bottom to top order"
[3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
'\x03\x04\x05\x00\x01\x02'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
3, 4, 5,
0, 1, 2,
Example for single band (calling with the full set of parameters):
>>> #
>>> img = Image.frombuffer("L", (3, 2), rawpb, 'raw', "L", 0, 1)
>>> list(img.getdata())
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
0, 1, 2,
3, 4, 5,
Changes to the original buffer object are reflected in this image:
>>> # change input buffer
>>> rawpb[0] = 255
>>>
>>> # changes to the original buffer object are reflected in this image.
>>> list(img.getdata())
[255, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>>
>>> img.tobytes("raw")
'\xff\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
>>>
>>> for y in range(2):
... for x in range(3):
... print(img.getpixel((x, y)), end=', ')
... print("")
...
255, 1, 2,
3, 4, 5,
Let me skip the example for multiple bands. Essentially, it is almost the same with the frombytes’s case.
See also: frombytes.
Image processing¶
alpha_composite¶
from PIL import Image
#
img1 = Image.open('data/srcimg10.png')
r, b, g = img1.split()
a = Image.new("L", r.size, "white")
img1 = Image.merge("RGBA", (r, b, g, a))
# img2 has alpha
img2 = Image.open('data/srcimg09.png')
img2 = img2.resize(img1.size)
#
Image.alpha_composite(img1, img2).save(
"result/Image_alpha_composite_01.png")
|
|
blend¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.blend, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.blend
import sys
from PIL import Image
#
alpha = float(sys.argv[1])
img1 = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
img2 = Image.open('data/srcimg02.jpg').resize(img1.size)
#
Image.blend(img1, img2, alpha).save(
"result/Image_blend_{}.jpg".format(alpha))
|
alpha=0.0 |
alpha=0.5 |
alpha=1.0 |
composite¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.composite, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.composite
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
# lower-triangle
data = np.tril(np.ones((256, 256)) * 255)
mask = Image.new("L", (256, 256))
mask.putdata(data.flatten().tolist())
mask.save("mask_tril_01.jpg")
|
mask_tril_01.jpg |
from PIL import Image
#
img1 = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
img2 = Image.open('data/srcimg02.jpg').resize(img1.size)
mask = Image.open('data/mask_tril_01.jpg')
mask = mask.resize(img1.size)
#
Image.composite(img1, img2, mask).save(
"result/Image_composite_01.jpg")
|
result |
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
mask = Image.new("L", (256, 256), "black")
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(mask)
draw.ellipse(
[0, 0, 256, 256], fill=255)
del draw
mask.save("mask_circle_01.jpg")
|
mask_circle_01.jpg |
from PIL import Image
#
img1 = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
img2 = Image.open('data/srcimg02.jpg').resize(img1.size)
mask = Image.open('data/mask_circle_01.jpg')
mask = mask.resize(img1.size)
#
Image.composite(img1, img2, mask).save(
"result/Image_composite_02.jpg")
|
result |
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
data = np.ndarray((256, 256))
for i in range(256):
data[i,:] = i
mask = Image.new("L", (256, 256))
mask.putdata(data.flatten().tolist())
mask.save("mask_grad_01.jpg")
|
mask_grad_01.jpg |
from PIL import Image
#
img1 = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
img2 = Image.open('data/srcimg02.jpg').resize(img1.size)
mask = Image.open('data/mask_grad_01.jpg')
mask = mask.resize(img1.size)
#
Image.composite(img1, img2, mask).save(
"result/Image_composite_03.jpg")
|
result |
eval¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.eval, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.eval
from PIL import Image
#
def func1(p):
return max(0, p - 50)
#
def func2(p):
return 255 - p
#
img = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
Image.eval(img, func1).save(
"result/Image_eval_01.jpg")
Image.eval(img, func2).save(
"result/Image_eval_02.jpg")
|
Image_eval_01.jpg |
Image_eval_02.jpg |
merge¶
- doc
https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/Image.html#PIL.Image.merge, http://effbot.org/imagingbook/image.htm#tag-Image.merge
from PIL import Image
#
img = Image.open('data/srcimg01.jpg')
r, g, b = img.split()
#
Image.merge("RGB", (b, g, r)).save(
"result/Image_merge_01.jpg")
|
|
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
#
img = Image.open('data/srcimg08.jpg')
r, g, b = img.split()
# build alpha image (with numpy)
ap = np.array(img.convert("L").getdata()).reshape(img.size)
ap[ap >= 128] = 255
ap[ap < 128] = 0
a = Image.new("L", img.size)
a.putdata(ap.flatten())
#
Image.merge("RGBA", (b, g, r, a)).save(
"data/srcimg09.png")
|
|
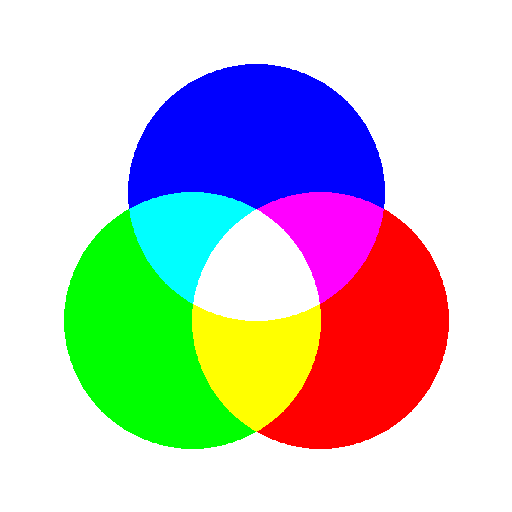
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageChops
dia = 128
circle = Image.new("L", (dia * 4, dia * 4), 0)
dctx = ImageDraw.Draw(circle)
dctx.ellipse([dia, dia, dia * 3, dia * 3], fill=255)
del dctx
offset = dia // 2
r = ImageChops.offset(circle, offset, offset)
g = ImageChops.offset(circle, -offset, offset)
b = ImageChops.offset(circle, 0, -offset)
dimg = Image.merge("RGB", (r, g, b))
mask = Image.eval(dimg.convert("L"), lambda p: 255 if p > 0 else 0)
dimg.putalpha(mask)
dimg.save("result/Image_merge_02.png")
|
|